7, Jan 2024
DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook
DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook
Related Articles: DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook
- 2025 And 2024: A Cinematic Odyssey
- 2025 Holiday Singapore: A Futuristic Adventure
- Corporate Travel Trends 2025: Embracing Agility, Sustainability, And Digitalization
- Public Holidays In Western Australia 2025
- Who Will Craft The JEE Advanced 2025 Paper: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook
DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook
![2025 DOE technical targets of PEM fuel cells [144]. Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342558295/figure/download/tbl5/AS:908110285774856@1593521772211/2025-DOE-technical-targets-of-PEM-fuel-cells-144.png)
Introduction
Fuel cells have emerged as promising clean energy technologies due to their high efficiency, low emissions, and versatility in various applications. In recognition of their potential, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has set ambitious targets for fuel cell development and deployment by 2025. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the DOE’s fuel cell targets, exploring their significance, challenges, and implications for the future of clean energy.
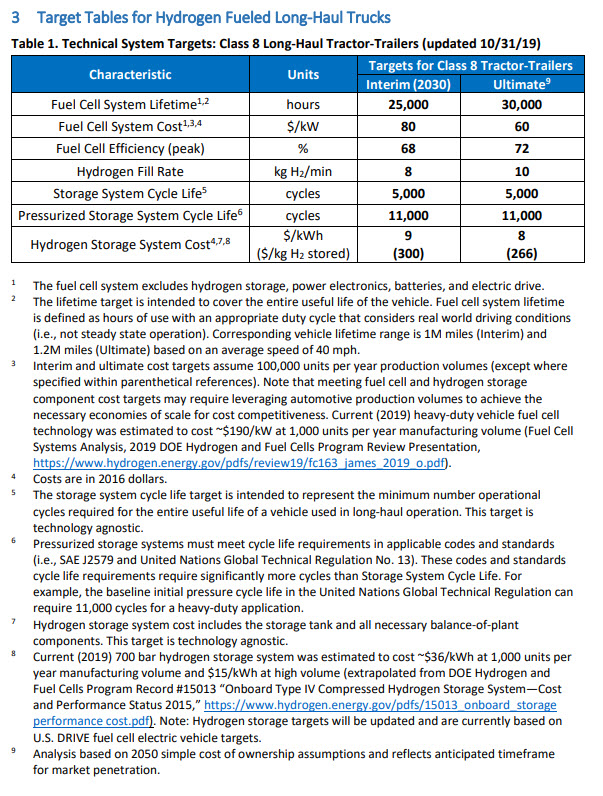
DOE’s 2025 Fuel Cell Targets
The DOE’s fuel cell targets for 2025 are outlined in the "Multi-Year Research, Development, Demonstration, and Deployment Plan for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells" released in 2017. The plan establishes specific goals for fuel cell performance, cost, and deployment:
Performance Targets:
- Increased Power Density: Fuel cells should achieve a power density of 3 kW/L for transportation applications and 5 kW/L for stationary applications.
- Improved Durability: Fuel cells should operate for at least 5,000 hours in transportation applications and 40,000 hours in stationary applications.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Fuel cells should achieve an electrical efficiency of 60% in transportation applications and 65% in stationary applications.
Cost Targets:
- Reduced Manufacturing Costs: Fuel cell systems should be manufactured for $40/kW in transportation applications and $25/kW in stationary applications.
- Lowered Operating Costs: Fuel cell systems should operate with a hydrogen cost of $2/kg and a total operating cost of less than $0.05/kWh.
Deployment Targets:
- Increased Fuel Cell Vehicle Production: 100,000 fuel cell vehicles should be produced annually in the United States.
- Expanded Hydrogen Infrastructure: 1,000 hydrogen fueling stations should be established across the country.
- Growing Stationary Power Capacity: 100 MW of fuel cell power capacity should be installed for stationary applications.
Significance of the Targets
The DOE’s fuel cell targets for 2025 are significant for several reasons:
- Accelerated Innovation: The targets drive research and development efforts to push the boundaries of fuel cell technology.
- Improved Cost Competitiveness: By setting ambitious cost targets, the DOE encourages the development of cost-effective fuel cell systems.
- Increased Market Adoption: The deployment targets aim to stimulate the growth of the fuel cell market and create a sustainable industry.
- Environmental Benefits: Widespread adoption of fuel cells will reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
Challenges to Achieving the Targets
Achieving the DOE’s fuel cell targets by 2025 presents several challenges:
- Technical Barriers: Overcoming the technical challenges associated with improving fuel cell performance, durability, and efficiency requires significant research and development efforts.
- Cost Reduction: Developing cost-effective manufacturing processes and supply chains is essential for making fuel cells commercially viable.
- Hydrogen Infrastructure Development: Establishing a robust hydrogen fueling infrastructure is critical for the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles.
- Public Acceptance: Raising awareness about the benefits of fuel cells and addressing concerns about safety and refueling infrastructure is crucial for market acceptance.
Implications for the Future
The successful achievement of the DOE’s fuel cell targets for 2025 will have significant implications for the future of clean energy:
- Decarbonization of Transportation: Fuel cell vehicles can significantly reduce carbon emissions from the transportation sector, contributing to the transition to a sustainable transportation system.
- Increased Energy Independence: Hydrogen produced from domestic resources can reduce dependence on foreign oil imports and enhance energy security.
- Economic Development: The growth of the fuel cell industry can create new jobs and stimulate economic activity.
- Improved Air Quality: Fuel cells emit only water vapor, making them ideal for reducing air pollution in urban areas.
Conclusion
The DOE’s fuel cell targets for 2025 represent a bold vision for the future of clean energy. By setting ambitious goals for performance, cost, and deployment, the DOE is driving innovation, stimulating market growth, and paving the way for a more sustainable and energy-independent society. Overcoming the challenges associated with achieving these targets will require collaboration among researchers, industry, and policymakers. With continued progress and commitment, the DOE’s fuel cell targets hold the promise of unlocking the full potential of fuel cell technology for a cleaner and more prosperous future.



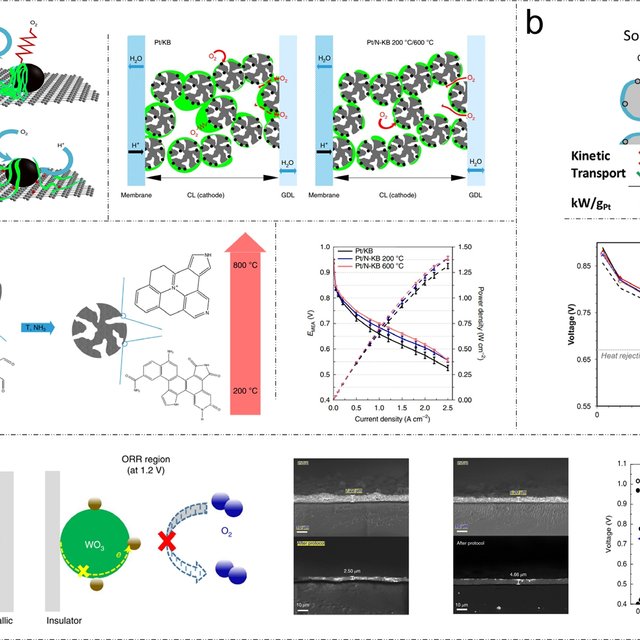
![2025 DOE technical targets of PEM fuel cells [144]. Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342558295/figure/fig3/AS:908110281576448@1593521771603/A-Steady-state-ORR-polarization-plots-bottom-and-H-2-O-2-yield-plots-top-measured_Q640.jpg)
![2025 DOE technical targets of PEM fuel cells [144]. Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342558295/figure/fig2/AS:908110281572353@1593521771570/Schematic-illustration-and-corresponding-HRTEM-images-of-the-mesoscale-ordering-during_Q640.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into DOE Fuel Cell Targets 2025: A Comprehensive Outlook. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin