25, Dec 2023
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process
Related Articles: Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process

Introduction
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are a type of electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy from a fuel source into electrical energy. They are a promising technology for clean and efficient power generation, with potential applications in vehicles, portable electronics, and stationary power plants.
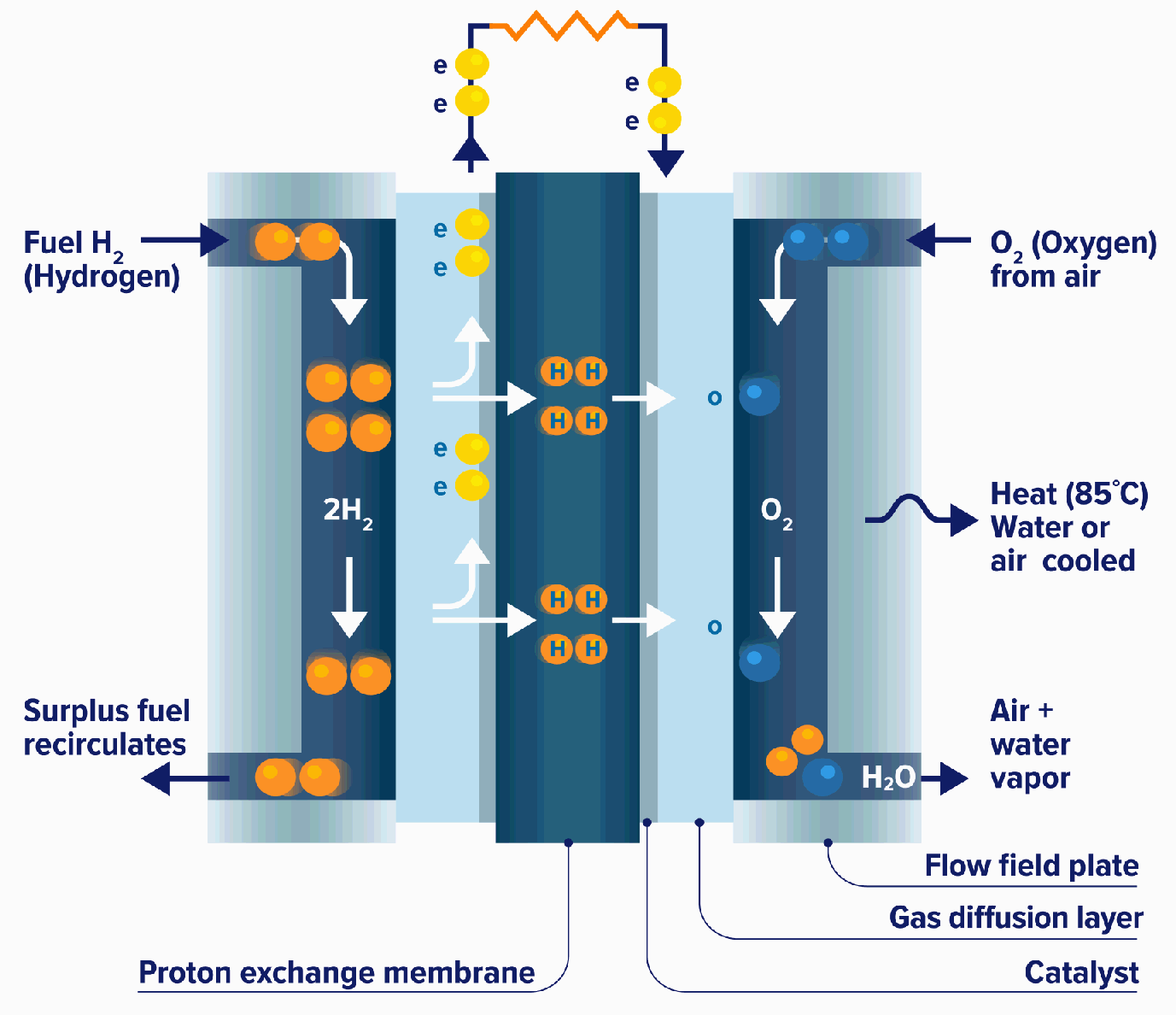
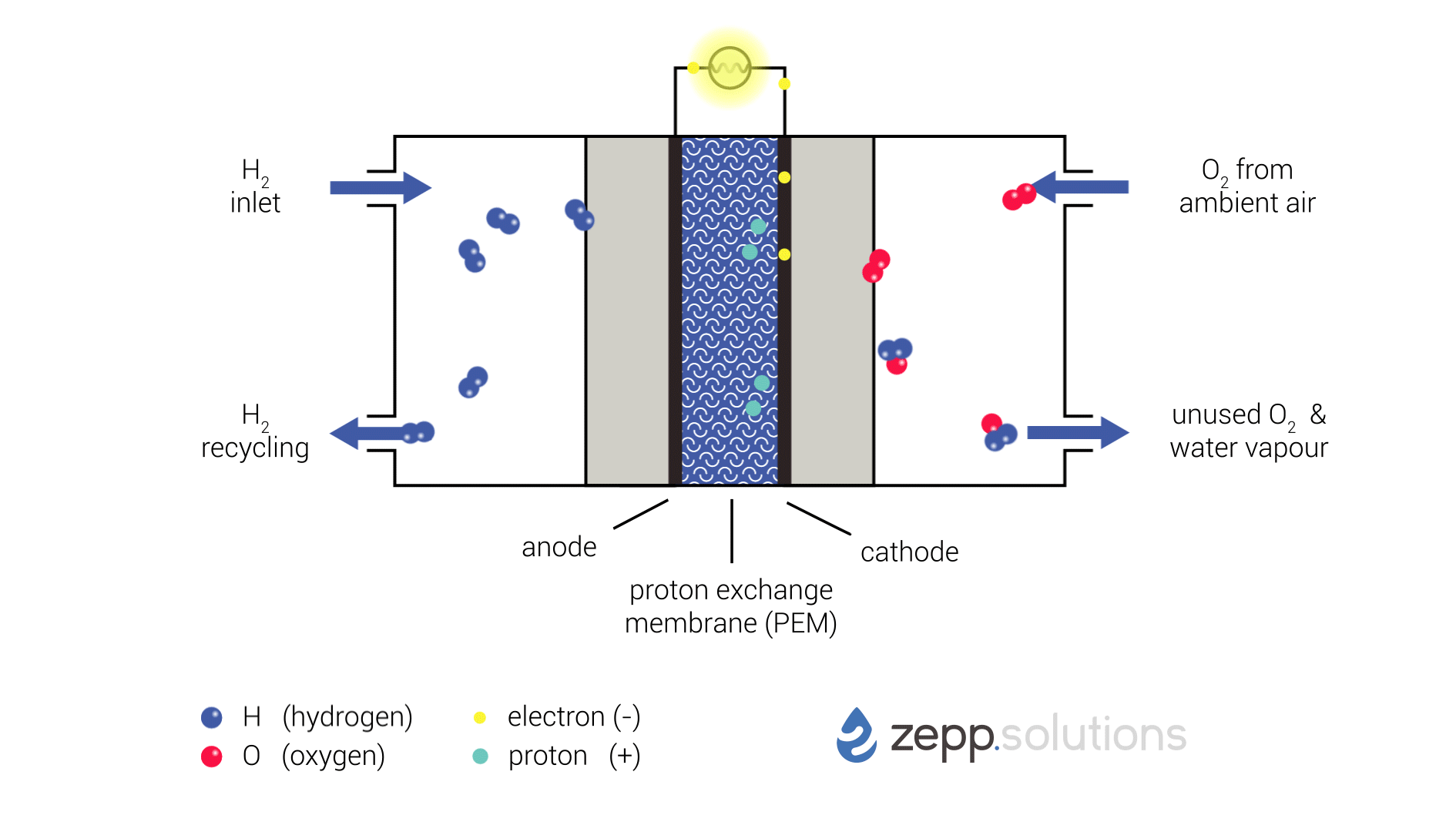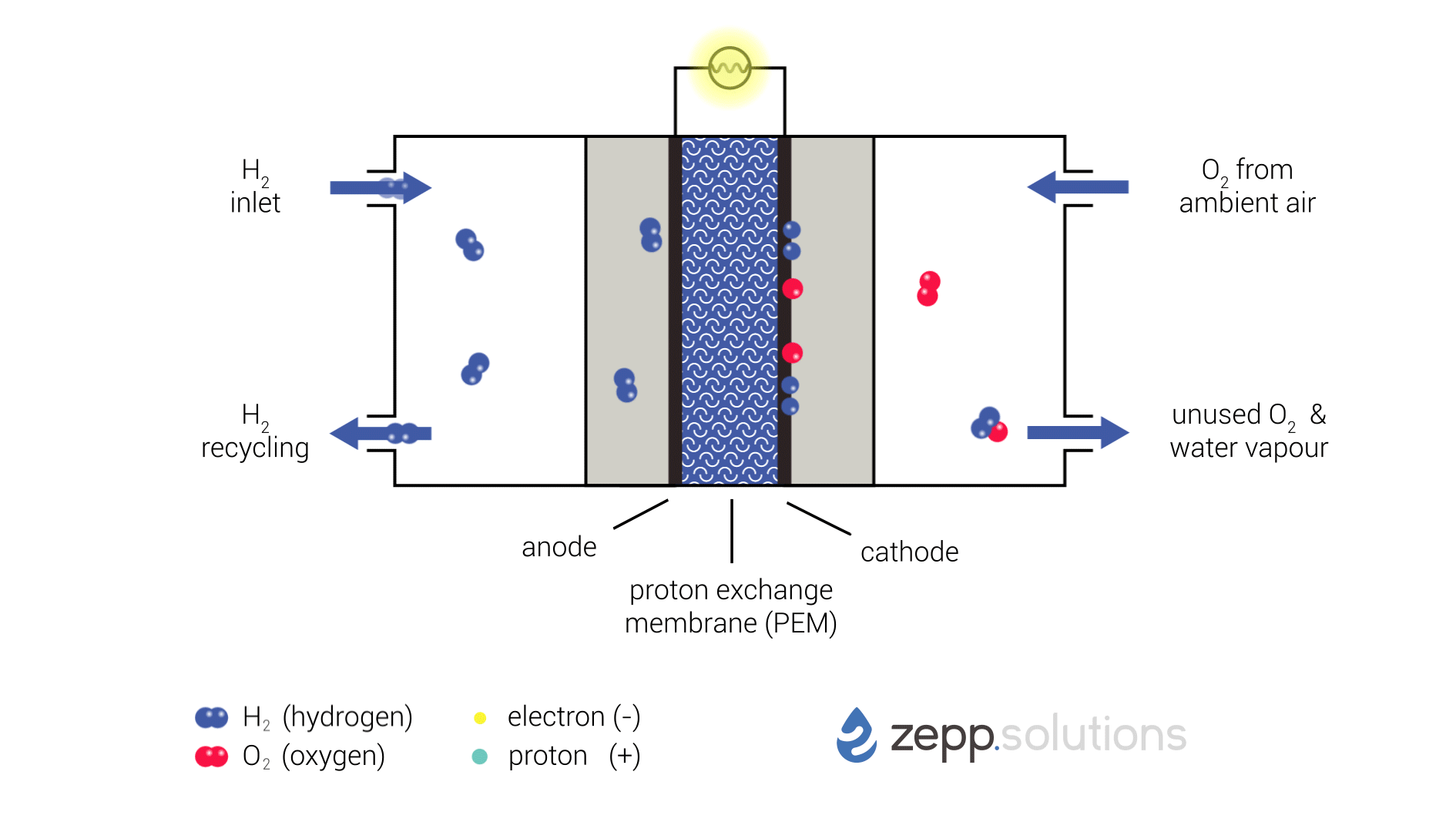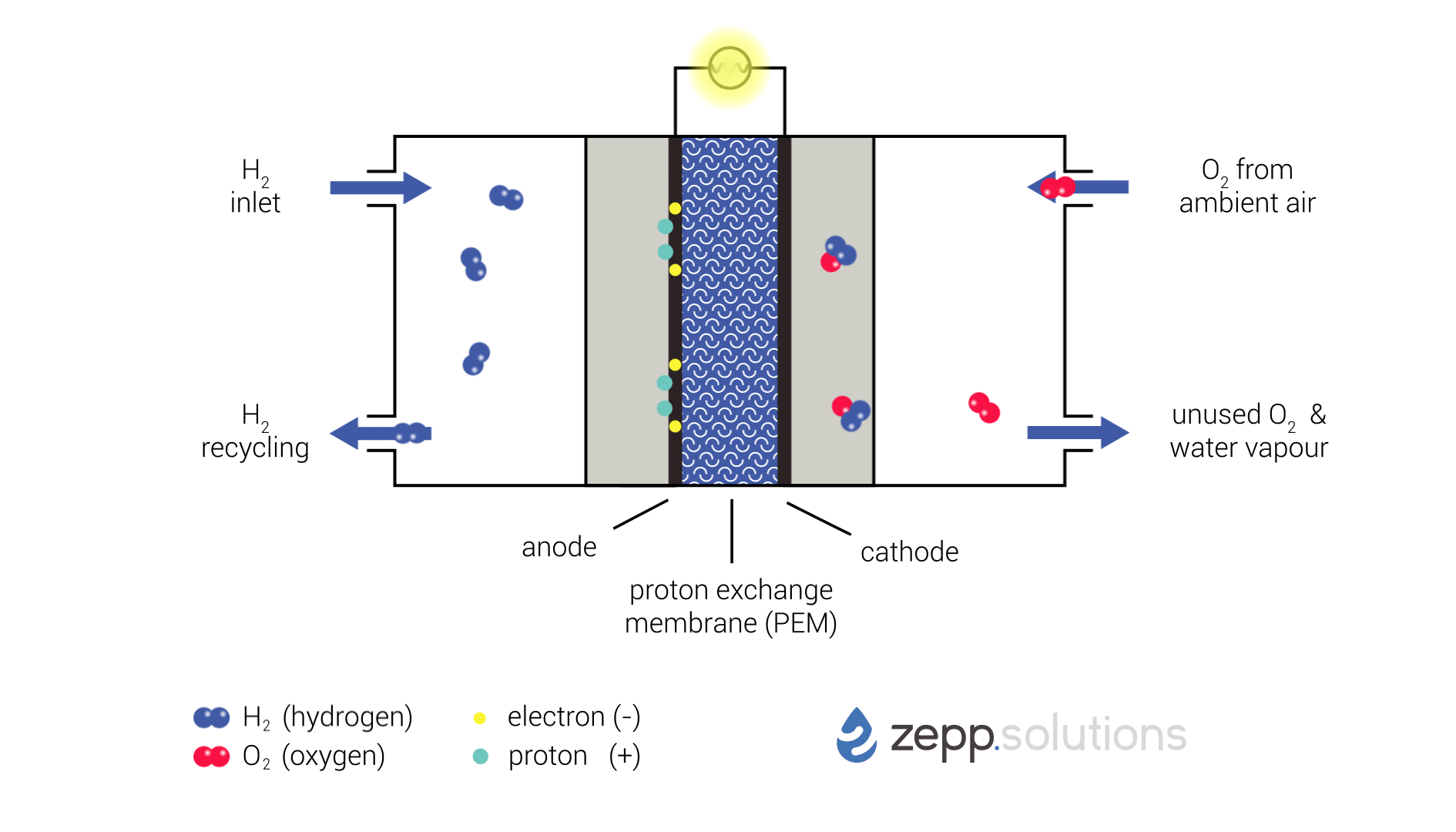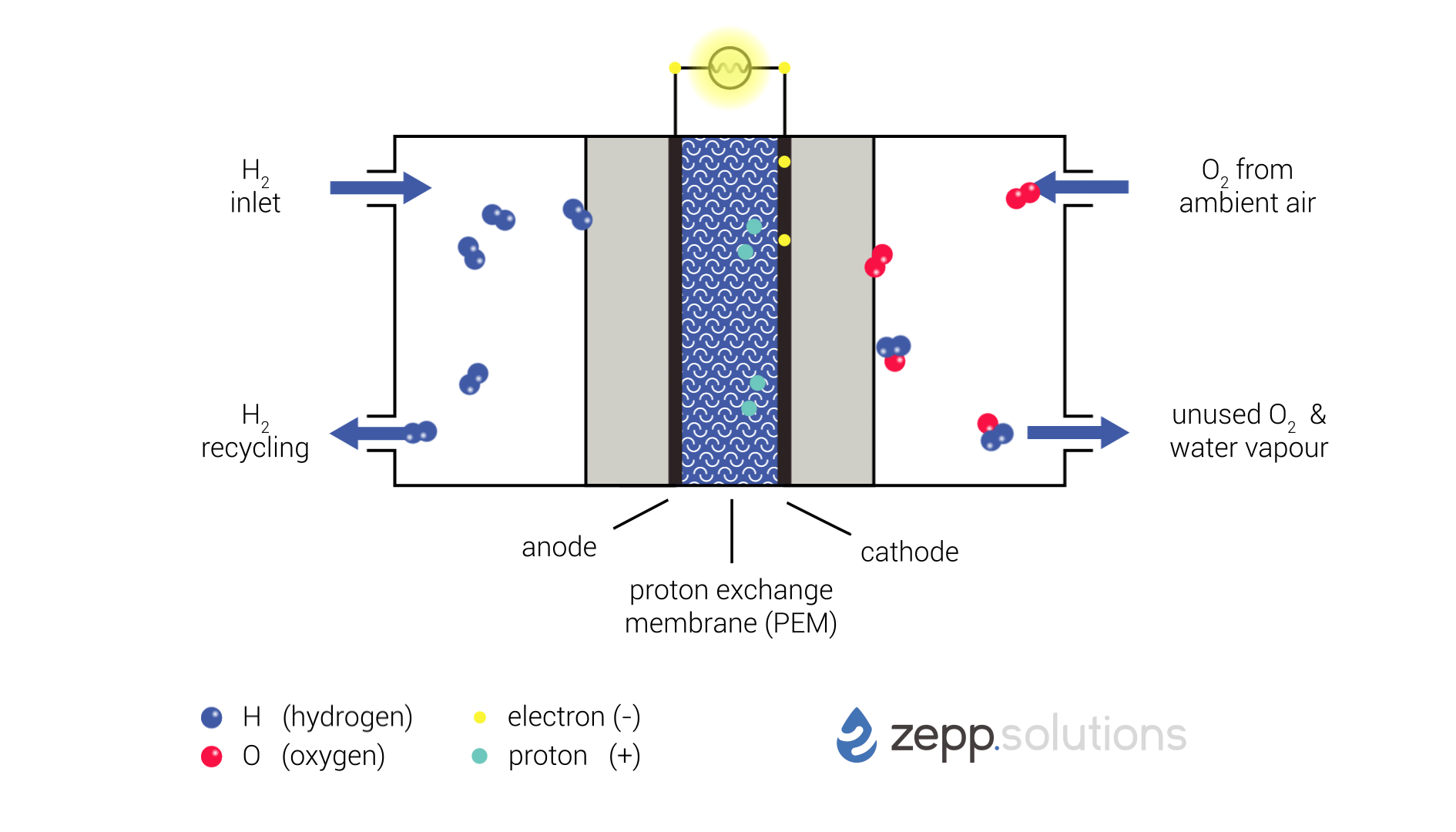
Fuel Cell Process
The PEMFC process involves the following steps:
- Fuel Supply: Hydrogen gas is supplied to the anode of the fuel cell.
- Anode Reaction: At the anode, hydrogen molecules react with a catalyst to form protons (H+) and electrons (e-):
H2 → 2H+ + 2e-- Proton Transport: The protons pass through a proton exchange membrane (PEM), which is a thin, acidic polymer that allows protons to pass through but blocks electrons.
- Oxygen Supply: Oxygen gas is supplied to the cathode of the fuel cell.
- Cathode Reaction: At the cathode, oxygen molecules react with protons and electrons to form water (H2O):
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O- Electrical Current: The electrons produced at the anode travel through an external circuit, creating an electrical current.
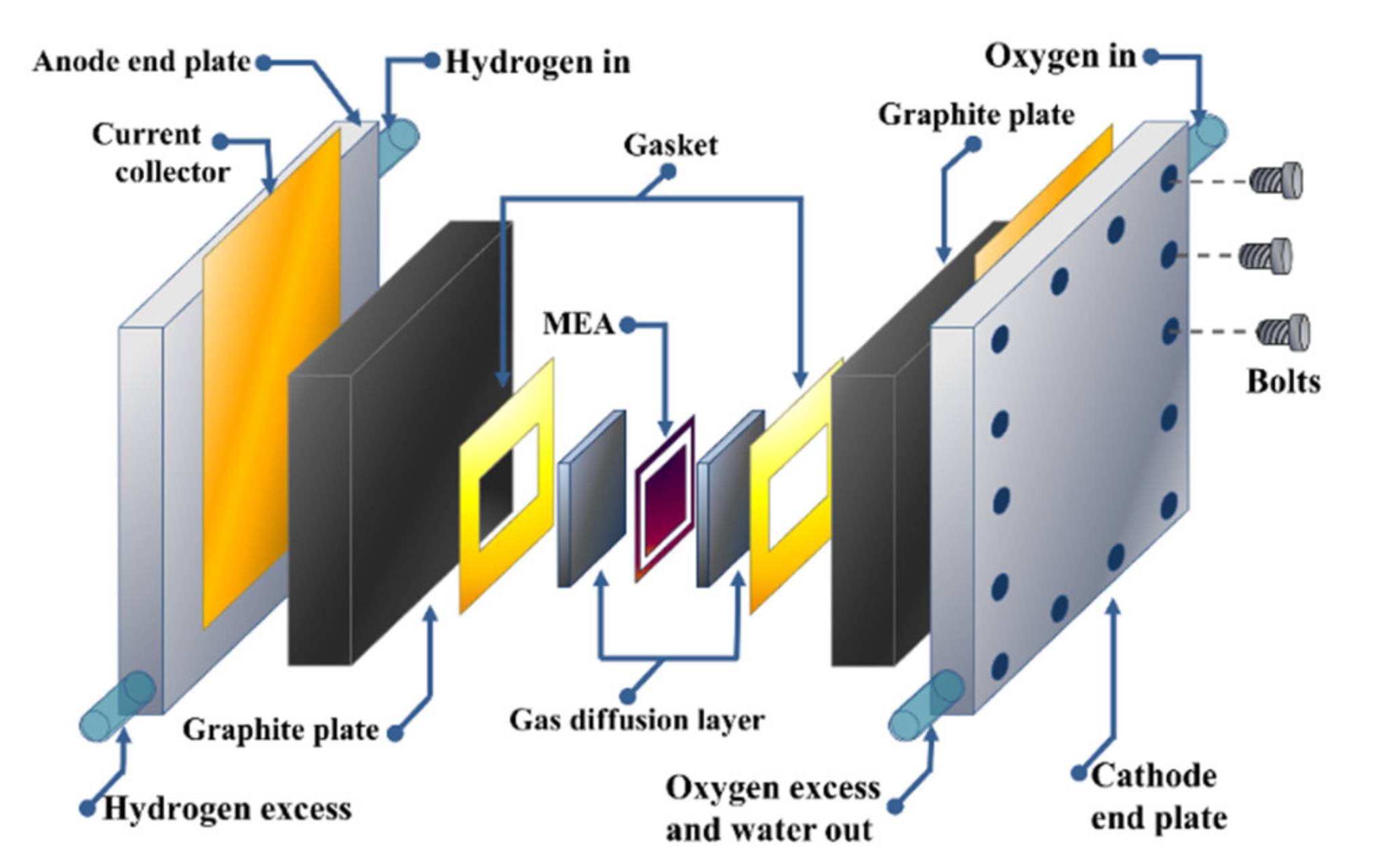
Components of a PEMFC
The main components of a PEMFC are:
- Anode: A porous electrode where the hydrogen oxidation reaction occurs.
- Cathode: A porous electrode where the oxygen reduction reaction occurs.
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM): A thin, acidic polymer that allows protons to pass through but blocks electrons.
- Gas Diffusion Layers: Porous layers that allow gases to reach the electrodes.
- Current Collectors: Conductive plates that collect electrons from the anode and cathode.
Advantages of PEMFCs
PEMFCs offer several advantages over other types of fuel cells:
- High Efficiency: PEMFCs have a high energy conversion efficiency, typically around 50-60%.
- Low Operating Temperature: PEMFCs operate at relatively low temperatures (80-100°C), which makes them easier to start and maintain.
- Compact Size: PEMFCs are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
- Zero Emissions: PEMFCs produce only water as a byproduct, making them an environmentally friendly technology.
Challenges of PEMFCs
PEMFCs also face some challenges:
- Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen gas is difficult to store and transport, which limits the widespread use of PEMFCs.
- Cost: PEMFCs are currently expensive to produce, but costs are expected to decline as the technology matures.
- Durability: PEMFCs have a limited lifespan, which needs to be improved for long-term applications.
Applications of PEMFCs
PEMFCs have a wide range of potential applications, including:
- Transportation: PEMFCs are being developed for use in electric vehicles, providing a clean and efficient alternative to gasoline-powered cars.
- Portable Power: PEMFCs can be used to power laptops, cell phones, and other portable electronic devices.
- Stationary Power: PEMFCs can be used as a backup power source for hospitals, data centers, and other critical facilities.
Conclusion
PEMFCs are a promising technology for clean and efficient power generation. They have a number of advantages, including high efficiency, low operating temperature, and zero emissions. However, challenges such as hydrogen storage, cost, and durability need to be addressed for PEMFCs to become widely adopted. As these challenges are overcome, PEMFCs are expected to play an increasingly important role in the transition to a clean energy future.


![[pib] Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) - Civilsdaily](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/c7/3e/83/c73e8327e0f7686c1dd5cde41441456a.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) Process. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
- 0
- By admin